Food Sources for Vital Nutrients
A varied diet ensures you obtain a broad spectrum of nutrients. Different food groups provide different nutritional profiles:
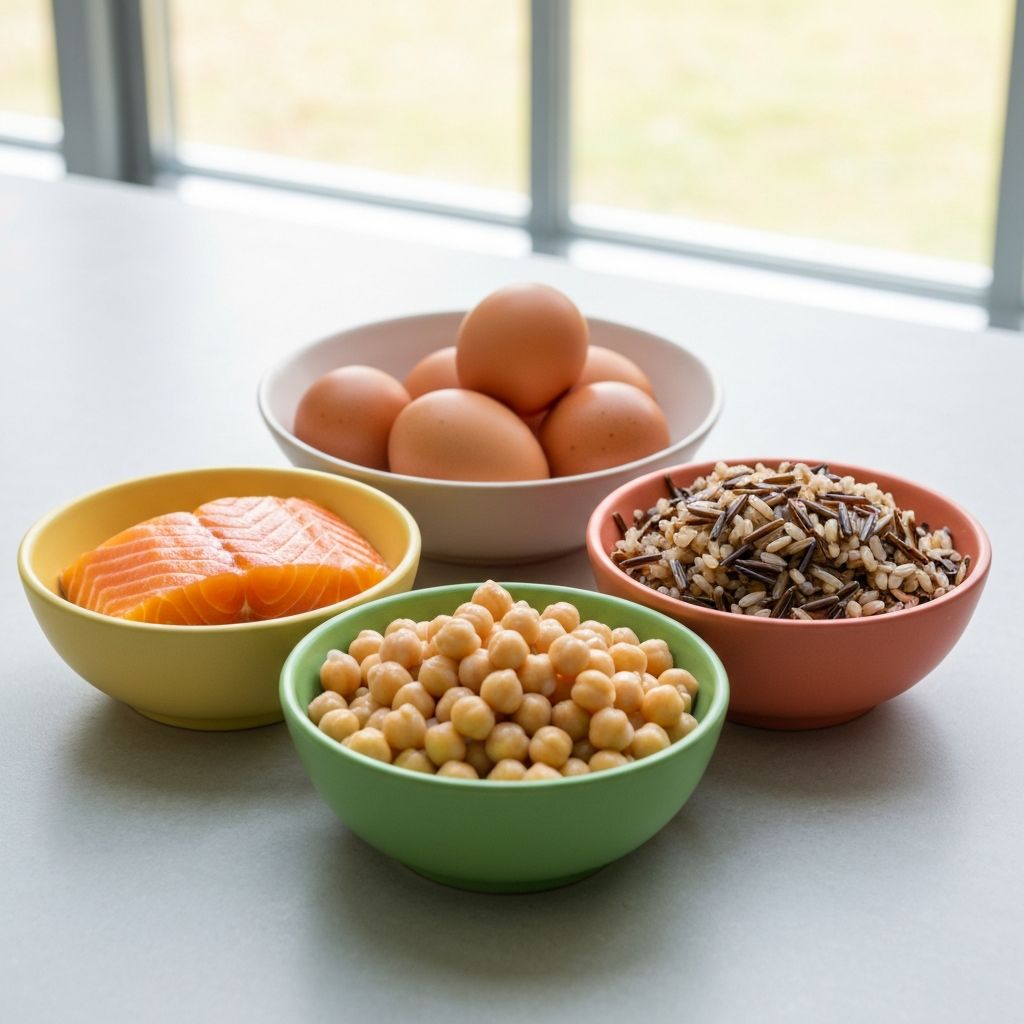
- Proteins: Lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, dairy
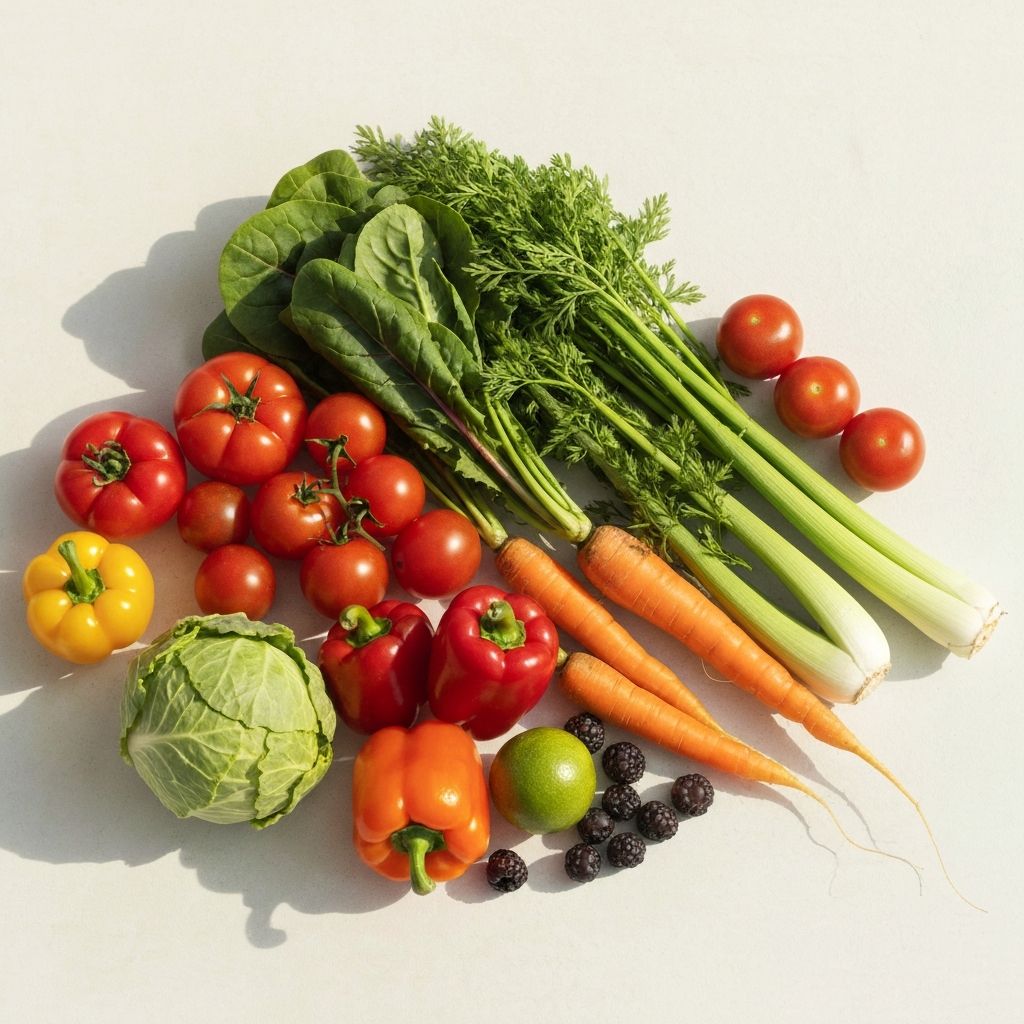
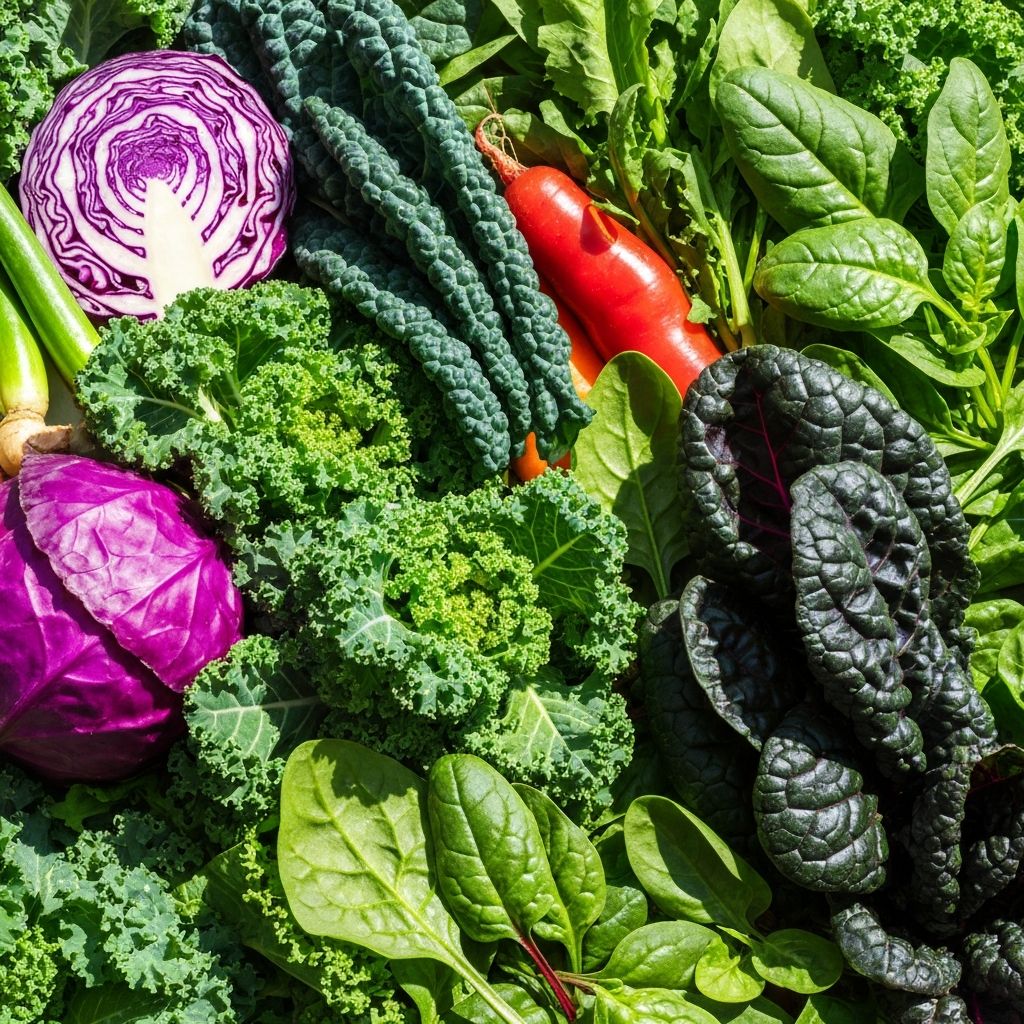
- Vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, peppers, tomatoes
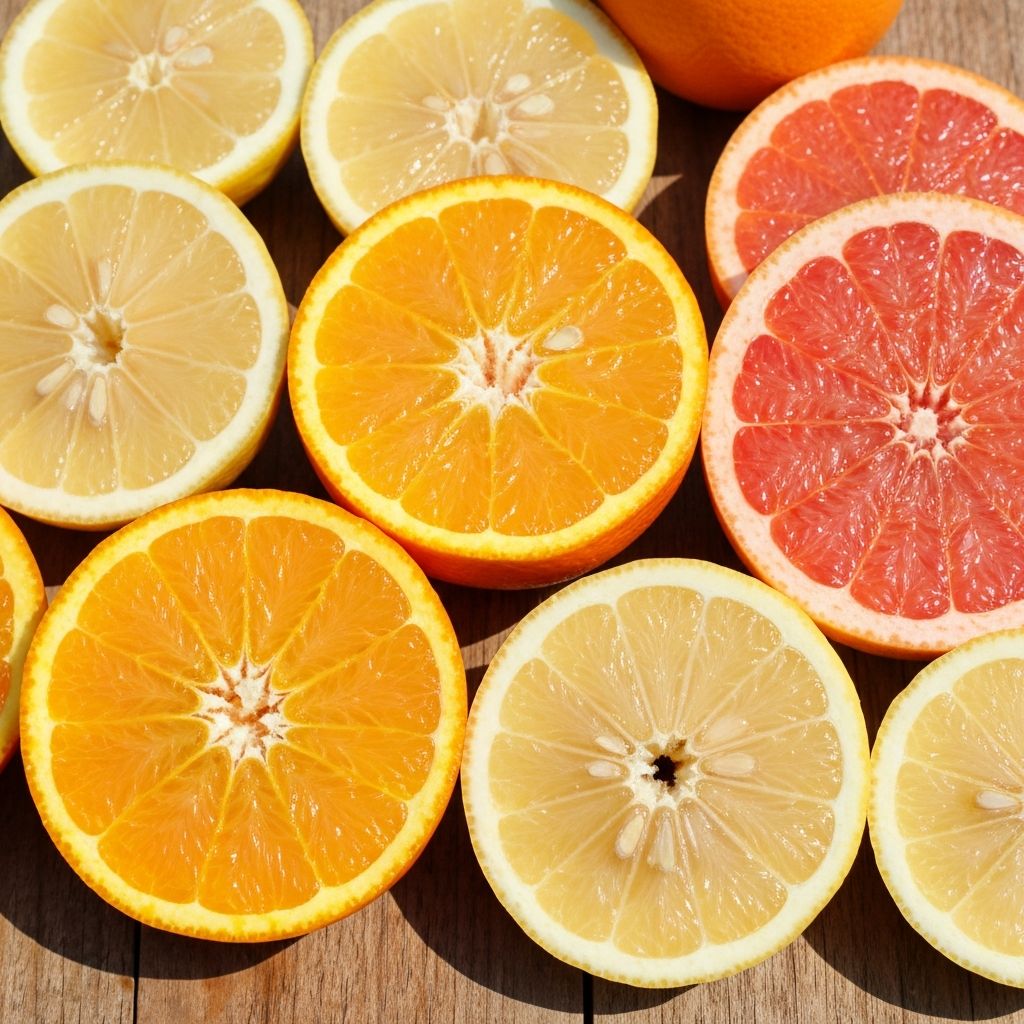
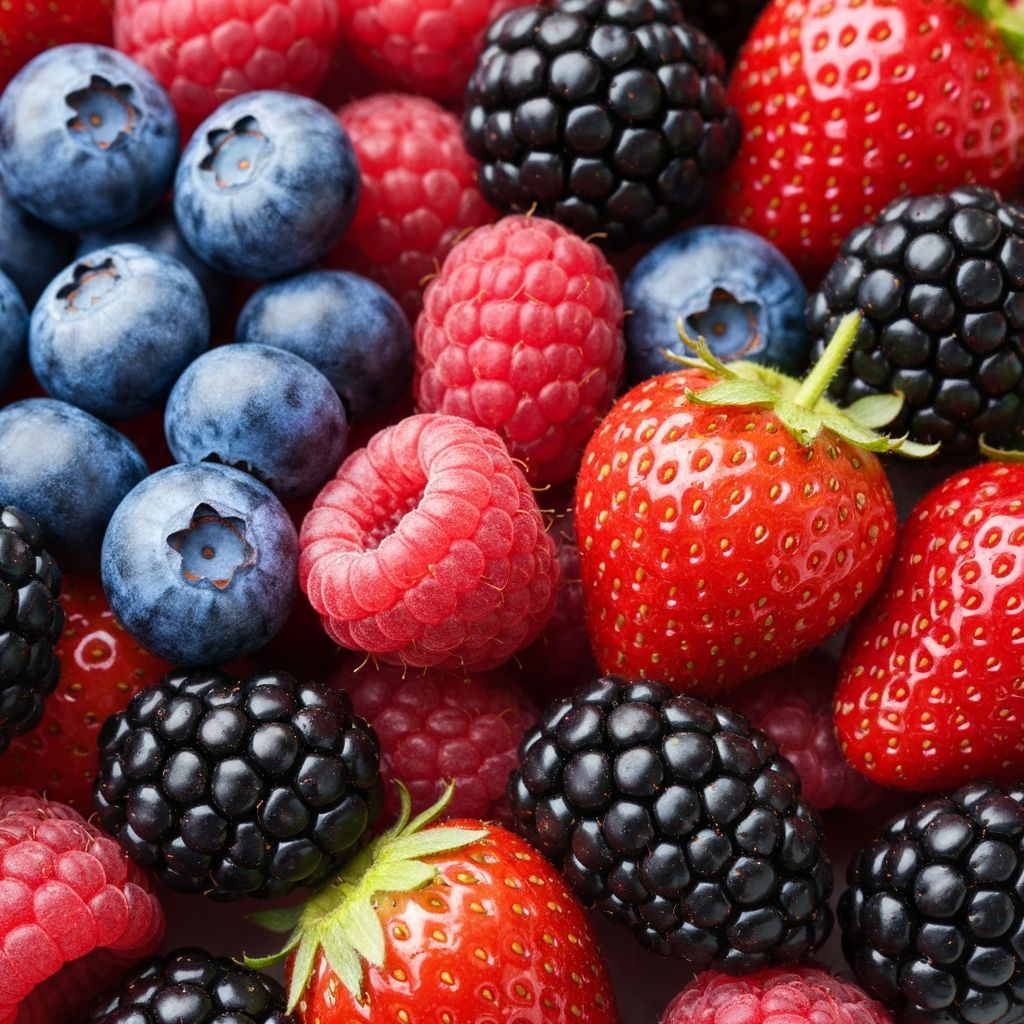
- Fruits: Berries, citrus, apples, bananas, avocados
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, oats, whole wheat, quinoa
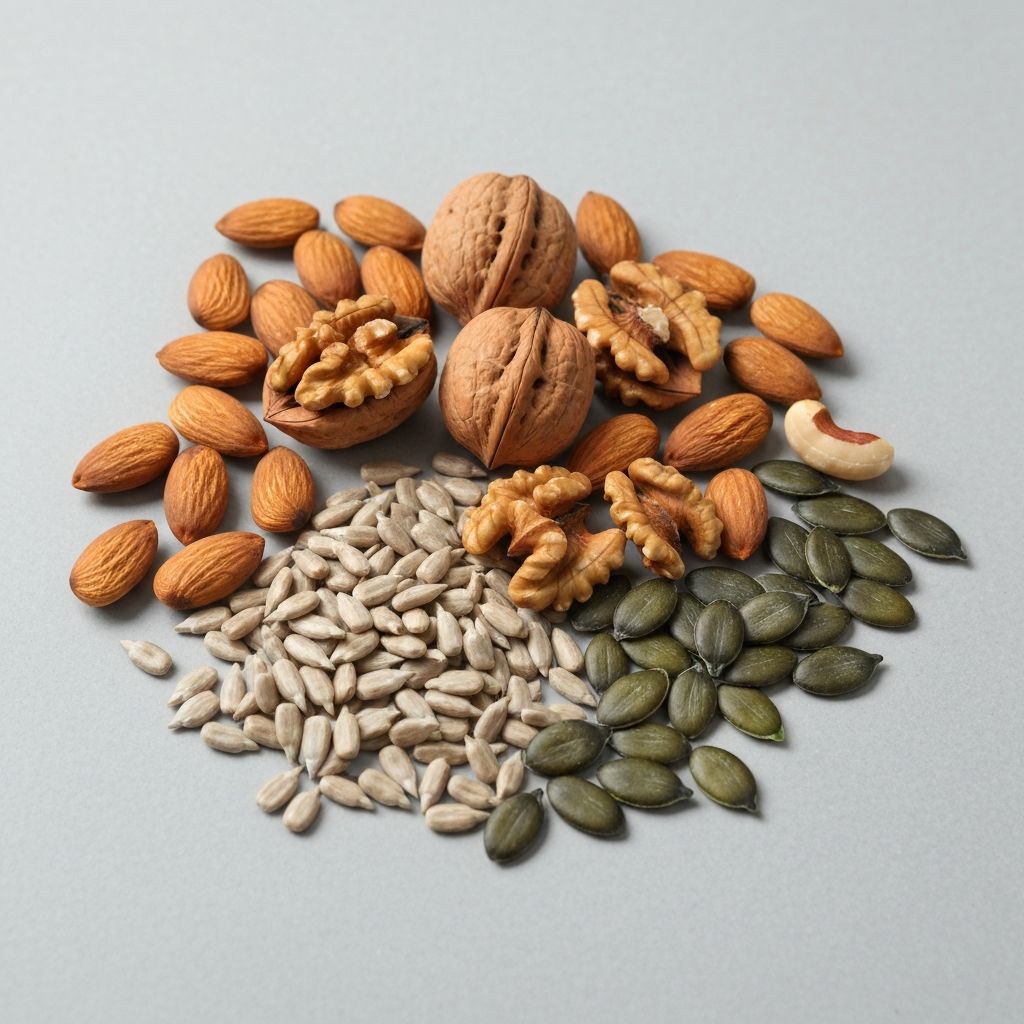
- Healthy Fats: Nuts, seeds, olive oil, fatty fish